The Post-Pandemic Rise of Blended Learning for Corporations and Higher Education
If you're familiar with online learning, you have also likely heard about blended learning.
While blended learning has been in practice for a long time, it has recently come into its own as a key part of learning following the COVID-19 pandemic.
Today, blended learning is talked about more than ever as the approaches to supporting learning experiences change and remote work continues to develop.
This article addresses the evolution of blended learning post-pandemic and its role in workplace and classroom settings.
What Is Blended Learning?
Blended learning is an approach that mixes face-to-face instruction with technology-mediated learning activities.
Also sometimes called hybrid learning, blended learning is a formal education experience where students learn:
- Partly through online learning (materials and opportunities), with control over the place, time, pace, and/or path,
- Partly in a supervised, traditional, place-based classroom/location away from home,
- The modalities in each student's learning path within a subject/course are connected to give the learner an integrated learning experience.
Blended learning gained more traction after the COVID-19 pandemic both in workplace and at school learning activities.
Examples of Blending Learning Content Delivery Methods
- Webcasting
- Webinars
- Online videos (live and recorded)
- Face-to-face (F2F) workshops, virtual workshops, and flipped workshops
- Learning apps
- Forums and communities
History of Blended Learning
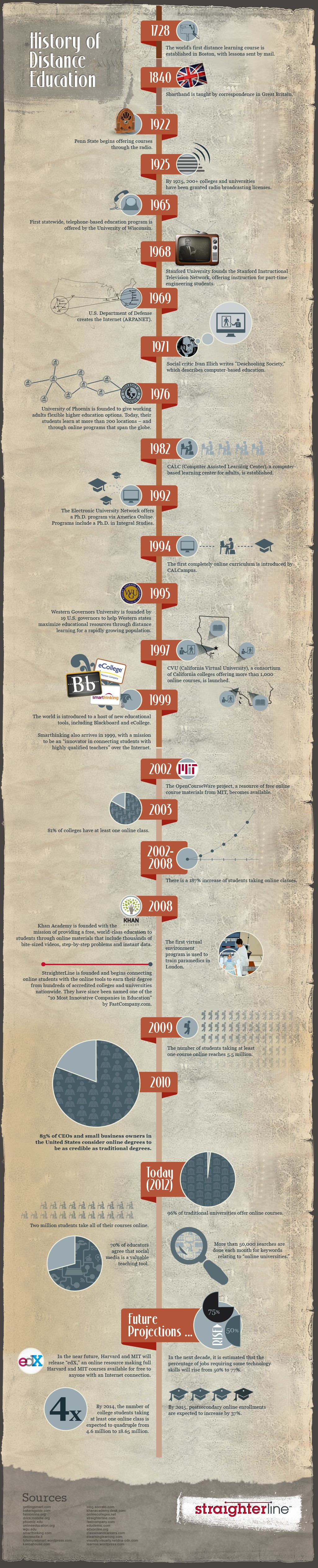
Post-Pandemic Evolutions of Blended Learning
Like many other sectors, the COVID-19 pandemic affected learning and training in transformative ways.
During the pandemic, many learning institutions were unable to deliver in-person learning as they had previously done.
In order to continue meeting the needs of learners, they had to seek alternative learning and education delivery methods.
Supported by increased technology usage in learning and training, blended learning became widely used and will likely be used more frequently in the future.
Blended learning design requires accounting for three important learner characteristics.
- independence in learning,
- responsibility, and
- self-discipline.
Engagement in Learning
Education has been delivered through practice and games over the years.
Blended learning now incorporates immersive technology to apply many other practices, games, and other learning methods to enhance learners' engagement.
In addition, instructional designers can create learning tools and online courses that fascinate learners.
Courses are streamlined, have more graphics, dialogue simulations, better audio, and more practice for engagement.
Flexibility In Learning, Less Standardization
While standards are essential for education, they sometimes fail to consider learners' needs, capabilities, preferences, or diversity.
Blended learning provides learners with the flexibility to enhance the path, place (location), time, pace, environment, and independence of learning experiences.
For example, learners no longer have to sit through the same but can choose when to learn in comfort and during less demanding work times.
Learners can move at their pace because of using recorded videos.
Quick learners can take another topic or practical tasks to train their skill, while struggling learners can revise the materials at their pace.
Motivation and Collaboration
Blended learning provides an interactive experience through collaboration between the learners and motivation from instructors via online training/learning platforms.
Learners are motivated to learn with a result in mind, such as getting knowledge, gaining extra skills, earning a promotion, etc.
LMS applications also allow gamification of learning to award learners for their progress.
This can help motivate learners to gain ownership in their learning process.
Skills-Based Learning, Innovation, and Model Experimentation
With global digitization, education is changing its greater focus to skill-based learning to support the economy and work environment.
It's expected that more innovation will arise as organizations settle into hybrid learning models and give their audiences more experimentation opportunities.
Interaction In Learning And Not Learning In Isolation
Isolation became a significant issue in learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.
This reduces interaction and student engagement.
In blended learning resources, materials, and opportunities for peer interaction capabilities are made available.
Examples include:
- Libraries and reading materials,
- Working in groups in Zoom,
- Collaboration on projects in a real-time LMS,
- Allowing learners to access other learning resources outside their textbooks,
- Giving students other avenues to learn and gain more knowledge.
Alternative School Ideas
Thanks to blended learning, physical schools and normal one-on-one classrooms have evolved.
Alternative school ideas developing around learning include:
- 'Unschool'
- Micro-schools
- learning pods
- Homeschooling
- 'Outschool'
These flexible alternative schooling ideas are expected to continue to increase as students are given more chances to determine their curriculum based on their interests and capabilities.
Online material and resources help enhance and support these students' learning.
Blended Learning in the Workplace
With an increase in hybrid work and remote work models, more employers are adopting blended learning in the workplace.
But since blended learning works differently in academia compared to corporate training, there's a need for particular blended learning programs in the workplace.
Blended learning in the workplace needs to support flexibility, adaptability, and provide accessibility.
Access to learning should be seamless, ubiquitous, and readily available.
Employees can engage in professional development activities such as reskilling and upskilling both while in the office or when working remotely.
But employers must ensure that employees are familiar with the apps or tools they'll use to access and participate in the learning and training before adopting them.
Blended learning can help improve employee onboarding and training because it combines different types of learning, such as:
- Hands-on learning,
- Virtual simulations,
- Group learning, and
- One-on-one sessions or instructor-led classroom sessions.
Examples Of Blended Learning In The Workplace
- Employee onboarding. Using video instruction or virtual simulation, one-on-one instruction, and hands-on learning practice to onboard employees.
- New equipment or work instruction. Employees are being introduced to new work procedures and principles using face-to-face instruction, with relevant online video and audio material and exercises with built-in collaboration and communication tools.
- Providing online learning resources to employees such as short courses before testing them on those new skills in practical exercises and procedures at work.
- Virtual workshops. Employees attend webinars and virtual workshops to learn and gain more knowledge.
Blended learning in the workplace needs to improve employee morale, boost their skills, and connect workers in a fun way.
Combining online learning, face-to-face discussions, and gamification in mentoring, seminars, and on-the-job training can enhance workplace productivity.
Blended Learning in Higher Education
In higher education, blended learning has grown in popularity because of its effectiveness in accommodating an increasingly diverse student population.
It does this while also adding value to the student's learning environment and instructors' efficiency through online teaching resources.
Courses with blended learning are among the most popular choices for higher education students, especially those with work and life balance.
This popularity is partly because blended courses allow faculty and students to enjoy the flexibility and convenience of e-learning while retaining the benefits of the face-to-face experience.
But, to succeed, many blended courses have to be strategically aligned with a school's, department's, or college's goals, students' diversity, and needs.
The online tools in blended courses enhance student engagement and help ensure students' participation in course discussions.
They also improve collaborative learning.
In blended courses, students perform better, but electronic resources offer other advantages.
For example, faculty can use student performance analytics to study and understand student learning and identify students who need early intervention.
Face-to-face interactions in higher education's blended courses can take many different forms, such as:
- working problem sets,
- mini-lectures,
- investigating case studies,
- discussion,
- small group work.
The interactive digital technologies, web-based support, or technology-enhanced learning experiences include;
- Online discussion boards.
- Student response systems.
- Assignments that result in digital products.
- Software that grades students automatically.
- Wikis and blogs.
- Pre-recorded video or screen-cast lectures/training.
One type of blended course in higher education is the flipped course.
This model moves content traditionally presented through one-on-one lectures to the digital media format.
Students study these contents before the digital class and then spend class time working on problems or doing case studies.
Other forms of blended learning in higher education are:
- Project-based learning
- Active, digital-based learning
- Case-based learning
- Experiential learning
- Discussion-based teaching & learning
- Flipping your classroom
Is Blended Learning Effective?
As with any other method, blended learning has pros and cons.
Blended learning combines face-to-face training, self-paced learning, and technology-enhanced learning.
It's known to provide flexibility and convenience, recognize/consider learners' learning needs, capabilities, and preferences, and provide better engagement learning outcomes.
Education institutions and organizations implement blended learning strategies to maintain high levels of learner motivation and engagement.

.jpg)

.png)

